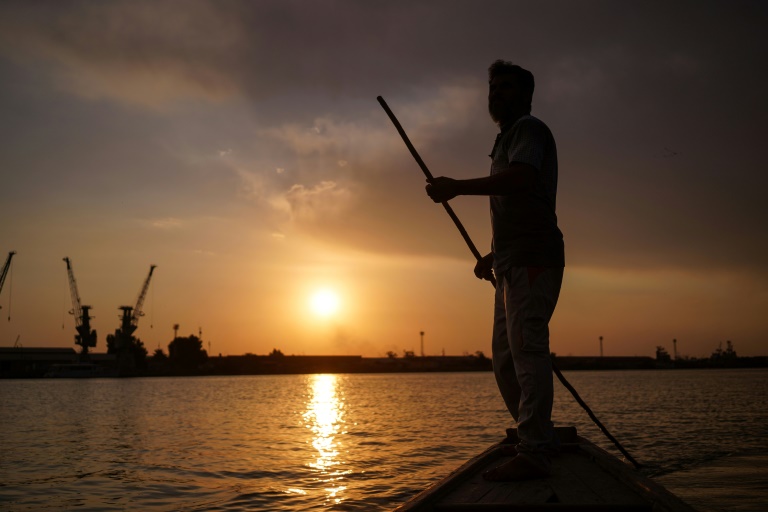
Sun setting on the Tigris: Iraqi fisherman Naim Haddad plys the Shatt al-Arab near Basra
It was the river that is said to have watered the biblical Garden of Eden and helped give birth to civilisation itself.
But today the Tigris is dying.
Human activity and climate change have choked its once mighty flow through Iraq, where — with its twin river the Euphrates — it made Mesopotamia a cradle of civilisation thousands of years ago.
Iraq may be oil-rich but the country is plagued by poverty after decades of war and by droughts and desertification.
Battered by one natural disaster after another, it is one of the five countries most exposed to climate change, according to the UN.
From April on, temperatures exceed 35 degrees Celsius (95 degrees Fahrenheit) and intense sandstorms often turn the sky orange, covering the country in a film of dust.
Hellish summers see the mercury top a blistering 50 degrees Celsius — near the limit of human endurance — with frequent power cuts shutting down air-conditioning for millions.
The Tigris, the lifeline connecting the storied cities of Mosul, Baghdad and Basra, has been choked by dams, most of them upstream in Turkey, and falling rainfall.
An AFP video journalist travelled along the river’s 1,500-kilometre (900-mile) course through Iraq, from the rugged Kurdish north to the Gulf in the south, to document the ecological disaster that is forcing people to change their ancient way of life.
– Kurdish north: ‘Less water every day’ –
The Tigris’ journey through Iraq begins in the mountains of autonomous Kurdistan, near the borders of Turkey and Syria, where local people raise sheep and grow potatoes.
“Our life depends on the Tigris,” said farmer Pibo Hassan Dolmassa, 41, wearing a dusty coat, in the town of Faysh Khabur. “All our work, our agriculture, depends on it.
“Before, the water was pouring in torrents,” he said, but over the last two or three years “there is less water every day”.
Iraq’s government and Kurdish farmers accuse Turkey, where the Tigris has its source, of withholding water in its dams, dramatically reducing the flow into Iraq.
According to Iraqi official statistics, the level of the Tigris entering Iraq has dropped to just 35 percent of its average over the past century.
Baghdad regularly asks Ankara to release more water.
But Turkey’s ambassador to Iraq, Ali Riza Guney, urged Iraq to “use the available water more efficiently”, tweeting in July that “water is largely wasted in Iraq”.
He may have a point, say experts. Iraqi farmers tend to flood their fields, as they have done since ancient Sumerian times, rather than irrigate them, resulting in huge water losses.
– Central plains: ‘We sold everything’ –
All that is left of the River Diyala, a tributary that meets the Tigris near the capital Baghdad in the central plains, are puddles of stagnant water dotting its parched bed.
Drought has dried up the watercourse that is crucial to the region’s agriculture.
This year authorities have been forced to reduce Iraq’s cultivated areas by half, meaning no crops will be grown in the badly-hit Diyala Governorate.
“We will be forced to give up farming and sell our animals,” said Abu Mehdi, 42, who wears a white djellaba robe.
“We were displaced by the war” against Iran in the 1980s, he said, “and now we are going to be displaced because of water. Without water, we can’t live in these areas at all.”
The farmer went into debt to dig a 30-metre (100-foot) well to try to get water. “We sold everything,” Abu Mehdi said, but “it was a failure”.
The World Bank warned last year that much of Iraq is likely to face a similar fate.
“By 2050 a temperature increase of one degree Celsius and a precipitation decrease of 10 percent would cause a 20 percent reduction of available freshwater,” it said.
“Under these circumstances, nearly one third of the irrigated land in Iraq will have no water.”
Water scarcity hitting farming and food security are already among the “main drivers of rural-to-urban migration” in Iraq, the UN and several non-government groups said in June.
And the International Organization for Migration said last month that “climate factors” had displaced more than 3,300 families in Iraq’s central and southern areas in the first three months of this year.
“Climate migration is already a reality in Iraq,” the IOM said.
– Baghdad: sandbanks and pollution –
This summer in Baghdad, the level of the Tigris dropped so low that people played volleyball in the middle of the river, splashing barely waist-deep through its waters.
Iraq’s Ministry of Water Resources blame silt because of the river’s reduced flow, with sand and soil once washed downstream now settling to form sandbanks.
Until recently the Baghdad authorities used heavy machinery to dredge the silt, but with cash tight, work has slowed.
Years of war have destroyed much of Iraq’s water infrastructure, with many cities, factories, farms and even hospitals left to dump their waste straight into the river.
As sewage and rubbish from Greater Baghdad pour into the shrinking Tigris, the pollution creates a concentrated toxic soup that threatens marine life and human health.
Environmental policies have not been a high priority for Iraqi governments struggling with political, security and economic crises.
Ecological awareness also remains low among the general public, said activist Hajer Hadi of the Green Climate group, even if “every Iraqi feels climate change through rising temperatures, lower rainfall, falling water levels and dust storms,” she said.
– South: salt water, dead palms –
“You see these palm trees? They are thirsty,” said Molla al-Rached, a 65-year-old farmer, pointing to the brown skeletons of what was once a verdant palm grove.
“They need water! Should I try to irrigate them with a glass of water?” he asked bitterly. “Or with a bottle?”
“There is no fresh water, there is no more life,” said the farmer, a beige keffiyeh scarf wrapped around his head.
He lives at Ras al-Bisha where the confluence of the Tigris and Euphrates river, the Shatt al-Arab, empties into the Gulf, near the borders with Iran and Kuwait.
In nearby Basra — once dubbed the Venice of the Middle East — many of the depleted waterways are choked with rubbish.
To the north, much of the once famed Mesopotamian Marshes — the vast wetland home to the “Marsh Arabs” and their unique culture — have been reduced to desert since Saddam Hussein drained them in the 1980s to punish its population.
But another threat is impacting the Shatt al-Arab: salt water from the Gulf is pushing ever further upstream as the river flow declines.
The UN and local farmers say rising salination is already hitting farm yields, in a trend set to worsen as global warming raises sea levels.
Al-Rached said he has to buy water from tankers for his livestock, and wildlife is now encroaching into settled areas in search of water.
“My government doesn’t provide me with water,” he said. “I want water, I want to live. I want to plant, like my ancestors.”
– River delta: a fisherman’s plight –
Standing barefoot in his boat like a Venetian gondolier, fisherman Naim Haddad steers it home as the sun sets on the waters of the Shatt al-Arab.
“From father to son, we have dedicated our lives to fishing,” said the 40-year-old holding up the day’s catch.
In a country where grilled carp is the national dish, the father-of-eight is proud that he receives “no government salary, no allowances”.
But salination is taking its toll as it pushes out the most prized freshwater species which are replaced by ocean fish.
“In the summer, we have salt water,” said Haddad. “The sea water rises and comes here.”
Last month local authorities reported that salt levels in the river north of Basra reached 6,800 parts per million — nearly seven times that of fresh water.
Haddad can’t switch to fishing at sea because his small boat is unsuitable for the choppier Gulf waters, where he would also risk run-ins with the Iranian and Kuwaiti coastguards.
And so the fisherman is left at the mercy of Iraq’s shrinking rivers, his fate tied to theirs.
“If the water goes,” he said, “the fishing goes. And so does our livelihood.”