Baby boom: the endangered wildlife revival at Cambodia's Angkor Wat
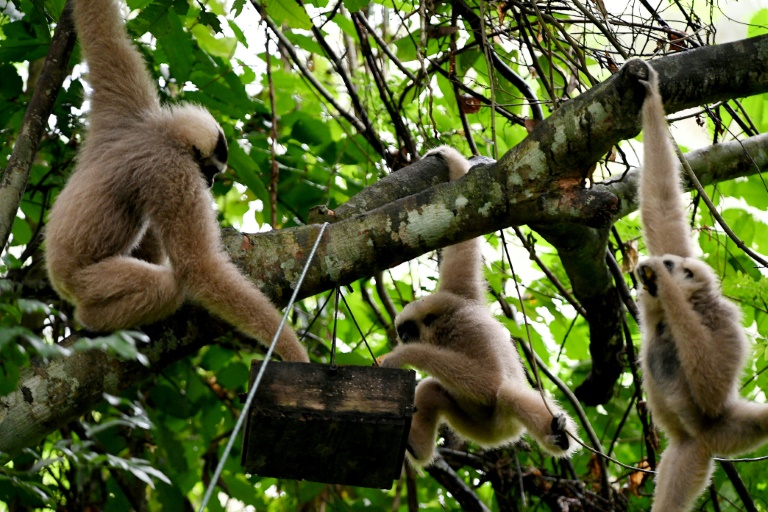
The melodic songs from families of endangered monkeys ring out over the jungle near Cambodia’s Angkor Wat temple complex — a sign of ecological rejuvenation decades after hunting decimated wildlife at the site.
The first pair of rare pileated gibbons were released in 2013 as part of a joint programme between conservation group Wildlife Alliance, the forestry administration and the Apsara Authority — a government agency that manages the 12th-century ruins.
The gibbon duo, named Baray and Saranick, were born from parents rescued from the wildlife trade and produced offspring a year later.
“We have now released four different pairs of gibbons within the Angkor forest and they have gone on to breed and now seven babies have been born,” Wildlife Alliance rescue and care programme director Nick Marx told AFP.
“We are restoring Cambodia’s natural heritage back into their most beautiful cultural heritage.”
Globally, gibbons are one of the most threatened families of primates, while the pileated gibbon is listed as endangered.
Marx says his team rescues some 2,000 animals a year and many more will soon call the Angkor jungle home.
There are hopes that once the baby gibbons reach sexual maturity in about five to eight years, they will also pair up and mate.
“What we are hoping for the future is to create a sustainable population of the animals… that we released here within the amazing Angkor forest,” Marx said.
– ‘Big victory’ –
Cambodian authorities have hailed the gibbon baby boom that began in 2014.
“This means a big victory for our project,” Chou Radina from the Apsara Authority said, adding that as well as gibbons, tourists could now see great hornbills flying over Angkor Wat.
The programme has released more than 40 other animals and birds including silvered langurs, muntjac deers, smooth-coated otters, leopard cats, civets, wreathed hornbills, and green peafowl.
All were rescued from traffickers, donated or born in captivity at the Phnom Tamao wildlife sanctuary near Phnom Penh.
The Angkor Archaeological Park — which contains the ruins of various capitals of the Khmer Empire, dating from the ninth to 15th centuries — has some of the oldest rainforest in Cambodia.
It is also the kingdom’s most popular tourist destination.
Since Angkor Wat became a world heritage site in 1992, its jungle, which covers more than 6,500 hectares, has benefited from increased legal and physical protections.
There are hopes that wildlife sightings will also spark interest in local and foreign tourists and boost conservation education efforts.
– Ongoing threats –
Rampant poaching, habitat loss from logging, agriculture and dam building has stripped much wildlife from Cambodian rainforests.
Last year, authorities removed 61,000 snare traps, environment ministry spokesman Neth Pheaktra said, adding that the government had launched a campaign to discourage hunting and eating of wildlife meat.
But widespread poverty even before the pandemic left many households without much choice but to continue hunting so their families could eat protein.
Animals are also hunted for traditional medicine and to be kept as pets.
According to Global Forest Watch, from 2001-2021 Cambodia lost 2.6 million hectares of tree cover, a 30 percent decrease since 2000.
Commercial interests are trumping protection efforts in some quarters — the Phnom Tamao zoo and wildlife rescue centre is under threat from a shadowy rezoning development plan, Marx said.
Back at Siem Reap — the gateway city to Angkor Wat — villager Moeurn Sarin shops at the market for bananas, watermelon, rambutan and fish to feed the pileated gibbon families and otters.
“We are happy to conserve these animals,” the 64-year-old said, adding he likes to watch the gibbons’ tree swinging antics.
“In the future, these animals will have babies for the young generation to see.”